Memantine: What It Is and Why It Matters
If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease, you’ve probably heard the name memristin… sorry, memantine. In simple terms, memantine is a prescription medication that helps protect brain cells from excess activity that can worsen memory loss.
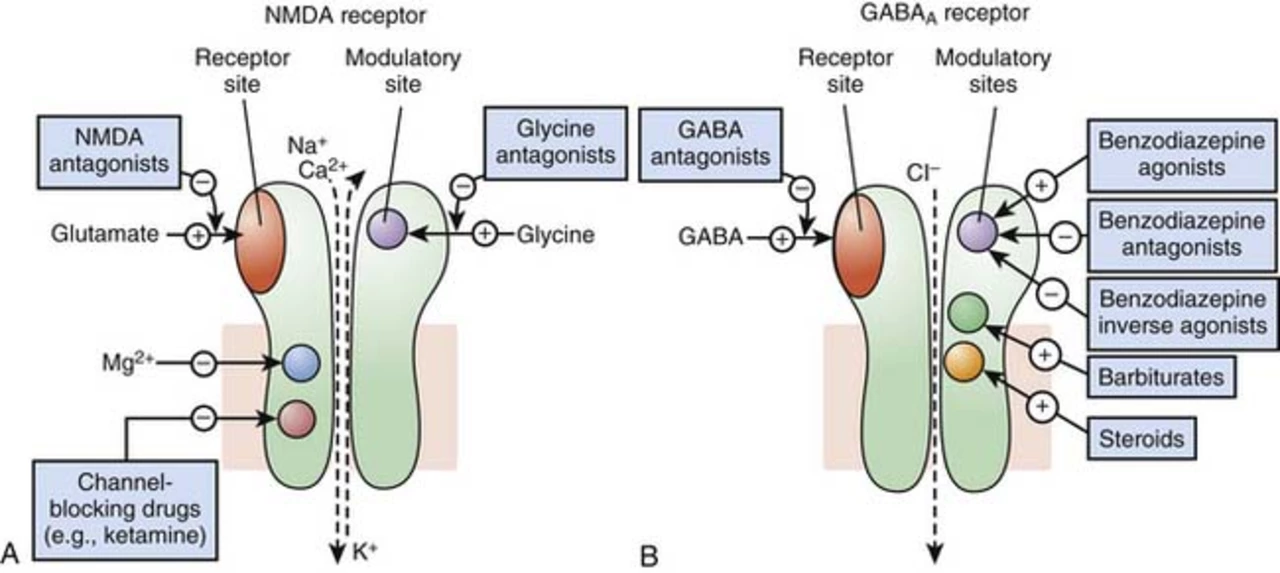
It belongs to a class called NMDA antagonists. Think of NMDA receptors as tiny doors on nerve cells; when they stay open too long, calcium floods in and damages the cell. Memantine gently blocks those doors so the brain isn’t over‑stimulated.
How Memantine Works
The drug doesn’t cure Alzheimer’s, but it can slow down certain symptoms like confusion, mood swings, and daily function decline. Doctors usually start with a low dose—5 mg once a day—to see how the body reacts, then gradually increase to the full 20 mg twice‑daily schedule.
Because memantine works on brain chemistry rather than blood pressure or cholesterol, it’s often added to other Alzheimer’s drugs such as donepezil. The combination can give a broader boost in cognition for some patients.
Key Things to Know Before You Start
Dosage basics: Take the tablets with or without food, at the same times each day. Skipping a dose? Just take it as soon as you remember unless it’s almost time for the next one—don’t double up.
Common side effects: You might feel dizziness, headache, constipation, or a mild rash. Most people notice these in the first week and they often fade. If anything feels severe—like trouble breathing or a fast heartbeat—call your doctor right away.
Drug interactions: Tell your pharmacist about all meds you’re on, especially other NMDA antagonists, antipsychotics, or medicines that affect the kidneys. Memantine is cleared by the kidneys, so kidney problems may require a lower dose.
Safety tips: Stay hydrated, keep a pill organizer handy, and set phone reminders if you have trouble remembering doses. If you’re caring for someone else, write down any changes in mood or behavior and share them with the healthcare team.
Pregnant or breastfeeding? Memantine hasn’t been studied enough to guarantee safety, so discuss alternatives with your doctor.
Sometimes people wonder if they can stop memantine abruptly. The short answer: don’t do it without talking to a professional. Stopping suddenly might cause a brief return of symptoms or withdrawal-like effects.
Many patients ask how long they’ll stay on the drug. There’s no set timeline—some use it for years, others switch if side effects outweigh benefits. Regular check‑ups help decide whether to keep going.
Lastly, remember that lifestyle still matters. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and mental activities can boost whatever benefit memantine provides.
In short, memantine is a useful tool in the Alzheimer’s toolbox. By understanding how it works, following dosage rules, and watching for side effects, you or your caregiver can make the most of what the medication offers.